Preparing a feasibility study for a private bilingual school requires a thorough and comprehensive analysis to ensure the project’s success and sustainability. The study begins with a comprehensive understanding of the target market, by identifying the number of potential students and assessing the area’s need for private education services. This is followed by a competitive analysis to assess the level of education provided by other schools, with a focus on identifying the differentiating factors that could give the proposed school a unique competitive advantage. The analysis also includes the financial aspect, by estimating the costs required to launch and operate the project and estimating projected revenues. The most appropriate funding sources must also be identified, whether through angel investors, bank loans, or other financing options.

A private bilingual school project is an integrated educational institution that provides high-quality education and meets the needs of parents seeking a distinguished education for their children. The project focuses on offering modern academic curricula that combine two different languages, while enhancing students’ linguistic, scientific, mathematical, and social skills. The importance of a private school project feasibility study lies in identifying potential investment opportunities and evaluating the financial resources required to establish and operate the project, in addition to developing marketing plans and strategies to attract target segments. The study also includes an analysis of the market and competitors to identify strengths and weaknesses, identify potential opportunities and threats, and develop the best plans to address them. The feasibility study also highlights the educational building equipment, human resource recruitment, outlines its organizational structure, and sets performance indicators. In conclusion, a project feasibility study enables investors to make informed decisions about the project and helps them achieve the desired strategic objectives.



Executive Summary
Study of project services/products
Market Size Study
Risk study
Technical study
Financial study
Organizational and administrative study
The Education Sector in the GCC Countries
Because Mashroo3k Economic Consulting and Market Research believes in the importance of the education sector and its role in localizing the national workforce, it has decided to present the following key indicators of the education sector in the GCC countries, calling for investment in this important sector:
The total number of students in early childhood development (including nurseries and kindergartens) in the GCC countries, according to the latest available statistics, reached 851,500 students.
The number of students in school levels in the GCC countries was estimated at approximately 9.3 million students (79.4% in the public sector and 20.6% in the private sector).
The number of students in adult education centers was estimated at approximately 181,247 students.
The number of higher education students was estimated at 2,206,446 students.
The number of early childhood teachers was estimated at 50,647.
The number of school teachers was estimated at approximately 727,904.
There are 5,806 existing early childhood education institutions.
There are 32,310 existing primary education institutions.
In recent years, governments in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries have sought to bridge the gap between education and the labor market. They have adopted educational curricula that increase the share of vocational and technical education and encourage learning through modern media and technologies. In this context, we should not fail to point out the increased spending in these six countries on education and its quality, in order to graduate generations that meet the private sector’s workforce needs.
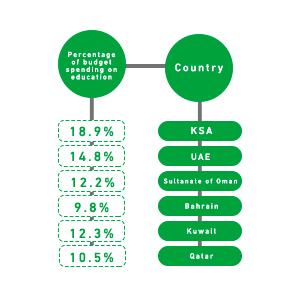
According to the latest statistics, Saudi Arabia spends 18.9% of its budget on education, the UAE spends 14.8% of its budget on education, the Sultanate of Oman spends 12.2% of its budget on education, Bahrain spends 9.8% of its budget on education, Kuwait spends 12.3% of its budget on education, and Qatar spends 10.5% of its budget on education. By 2023, the private education market in the GCC will reach $26.2 billion.
Global Education Sector
The global education services market was valued at approximately $2,882.52 billion by the end of 2021, and global experts expect the market to reach $3,191.79 billion by the end of 2022, achieving a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.7%. By 2026, the market will reach $4,623.90 billion, representing a CAGR of 9.7% over the forecast period.

By 2030, the global value of education as an industry will reach US$10 trillion.
By 2024, the value of online education worldwide will reach US$247.46 billion.
The AI education market will expand at a compound annual growth rate of 36% from 2022 to 2030.
In 2000, the number of students worldwide was approximately 657 million, and this number increased to 739 million in 2019.
In 2000, the number of secondary school students was approximately 452 million, and this number increased to 601 million in 2019.